edible hydrophobic coating
Edible super-hydrophobic coatings have attracted great attentions as they can avoid the waste of liquid foods such as honey and milk adhered to the inside of containers. This protective layer acts as a barrier between the food and external environment and thus delay the ripening and spoilage process.

Function And Usefulness Of Edible Film And Coatings In The Food Industry Download Scientific Diagram
Edible films are made by casting and the extrusion process and coating of the edible solution are done by dipping and spraying.

. Edible films and coatings have been used extensively in food industry to protect the quality and extend the shelf life of foods. In this work a thermo-resistant edible super-hydrophobic coating has been fabricated using beeswax and. The significant difference is that in edible film solid edible laminate is wrapped around the food products.
The coating matrix results in. Fruits and vegetables are coated in nature by a natural waxy coating called cuticle consisting of a layer of fatty acid-related substances such as waxes and resins with low permeability to water Baldwin 1994. Gestión en línea.
Superhydrophobic Coatings with Edible Biowaxes for Reducing or Eliminating Liquid Residues of Foods and Drinks in Containers. Peng Wang Xueren Qian and Jing Shen Biowaxes including carnauba wax and beeswax are edible and renewable. We used FDA-approved edible materials to fabricate superhydrophobic coatings in a simple low cost scalable single step process.
Wax was the first coating used in fruits specifically in citrus fruits. In contrast the edible coating forming solution is applied to the food product. 1 organic acids namely lactic acetic propionic benzoic sorbic 2 fatty acid esters such as glyceryl monolaurate 3 polypeptides such as peroxidase lysozyme lactoferrin nisin and 4 plant essential oils such as cinnamon.
Edible coatings are discussed for meats cheese fruit and vegetables confectionery bakery goods and fast food. Our coatings display high. Edible coatings as a structural matrix An edible coating is a thin layer of material that can be consumed and provides a barrier to moisture oxygen and solute movement for the food Falguera et al.
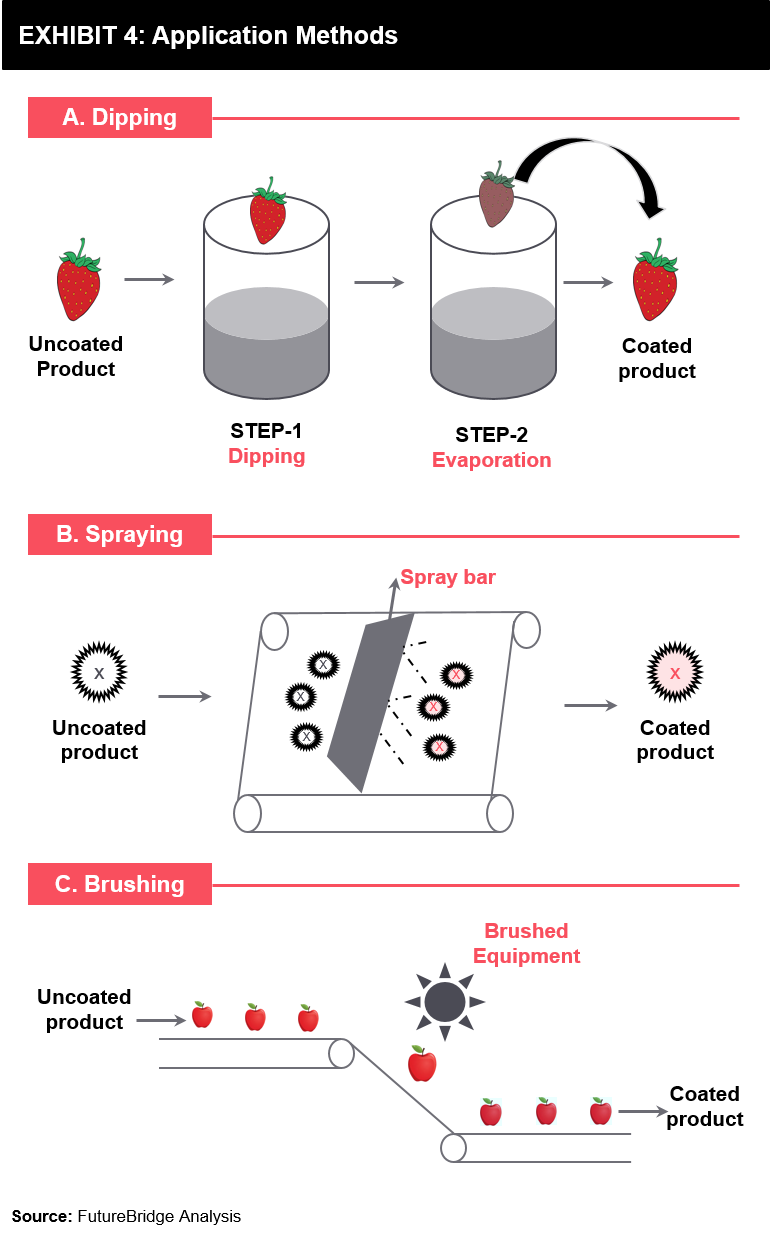
Dipping Figure 3a spraying Figure 3b and hand coating Figure 3c techniques are the most common methods for applying edible coatings to fresh fruits and vegetables. Foods such as minimally processed products are especially. It is free from waxes and has been designed with optimal hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance to achieve good water vapor resistance and barrier properties.
There are several categories of antimicrobials that can potentially be incorporated into edible coatings. Edible coatings could provide a barrier for moisture and gas or act as a vehicle to deliver colors flavors antioxidants. They are created entirely from food-grade ingredients such as proteins polysaccharides or lipids and are usually 5 nm thick.
The edible coating is a solution to improve the quality and shelf life of fresh produce ranging from meat poultry fish and dairy products to post-harvest fresh fruits and vegetables. Nevertheless their use can have more innovative uses beyond their current applications. Our coatings display high contact angles and low roll off angles for a variety of liquid products consumed daily and facilitate easy removal of liquids from food containers with virtually no residue.
Disclosed is an edible coating a food product coated with the coating and the method for manufacturing the food product. The nature of the gluten has significant. We used FDA-approved edible materials to fabricate superhydrophobic coatings in a simple low cost scalable single step process.
The coating comprises a first layer comprising first edible oil and a second layer comprising a hydrophobic edible particle wherein the hydrophobic edible particle has a diameter from 20 nm to 500 microns. Gelatin is a hydrophobic protein usually found in wheat which is also a globular protein and also used in some edible coatingsfilms due to its low cost and availability. Even at high concentrations our coatings are.
However the poor thermal stabilities of edible super-hydrophobic coatings restrict their applications. A very wide range of compounds is available for increasing the hydrophobicity of lipid-based edible films. Once dispersed in a polar solvent these natural materials could be easily converted into nontoxic roll-off and superhydrophobic.
The edible coating plays an important role as a gas barrier so it causes anaerobic respiration in fruits and vegetables which results in causing a delay in the ripening process. Other techniques such as fluidized bed and foaming are also available. Disclosed are an edible coating a food product coated with the coating and the method for manufacturing the food product.
This chapter discusses the materials preparation methods characteristics and applications of lipid-based edible films and coatings. In the last few years a great deal of interest has been given over to applying edible coatings to highly perishable food products. HPMCOA coatings containing 2 wv sodium benzoate SB 1 ammonium carbonate AC 1 potassium carbonate PC 1.
An edible coating can also be used as an effective carrier of many functional ingredients including antimicrobial agents antioxidants flavorings and colorants Chen 1995. In other words the team has created an effective phase change material PCM from natural materials. Composite edible coatings based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose HPMC as a polymeric phase and oleic acid OA or beeswax BW as a hydrophobic phase were formulated with different food additives as antifungal ingredients.
Edible coatings and films reduce packaging waste prevent the incorporation of chemical preservatives and result in a minimally-processed natural fresh product with an extended shelf life. Texcoat FV Pro is a proprietary triglyceride based edible coating. Gelatin coatings usually depict good transparency mechanical and barrier properties and can be manufactured via an extrusion or casting process.
In addition these coatings can store latent heat. The food product having the coating is. Professor Ilker Bayer from the Italian Institute of Technology in Genova Italy address these issues by forming hydrophobic and superhydrophobic smart coatings based on bees wax and water.
However these techniques are rarely used on commercial and laboratory scales 45. Edible films and coatings may be defined as protective layers created around food surface by applying solutions made from edible polymers like polysaccharides proteins lipids or their combinations.

Functional Food Packaging For Reducing Residual Liquid Food Thermo Resistant Edible Super Hydrophobic Coating From Coffee And Beeswax Sciencedirect

Superhydrophobic Coatings With Beeswax And Carnauba Wax Youtube

Combining Edible Coatings Technology And Nanoencapsulation For Food Application A Brief Review With An Emphasis On Nanoliposomes Sciencedirect

Pdf Edible Films And Coatings With Pectin

All Natural Superhydrophobic Coating For Packaging And Blood Repelling Materials Sciencedirect

Most Utilized Materials For Protein Based Edible Films And Coatings Download Scientific Diagram
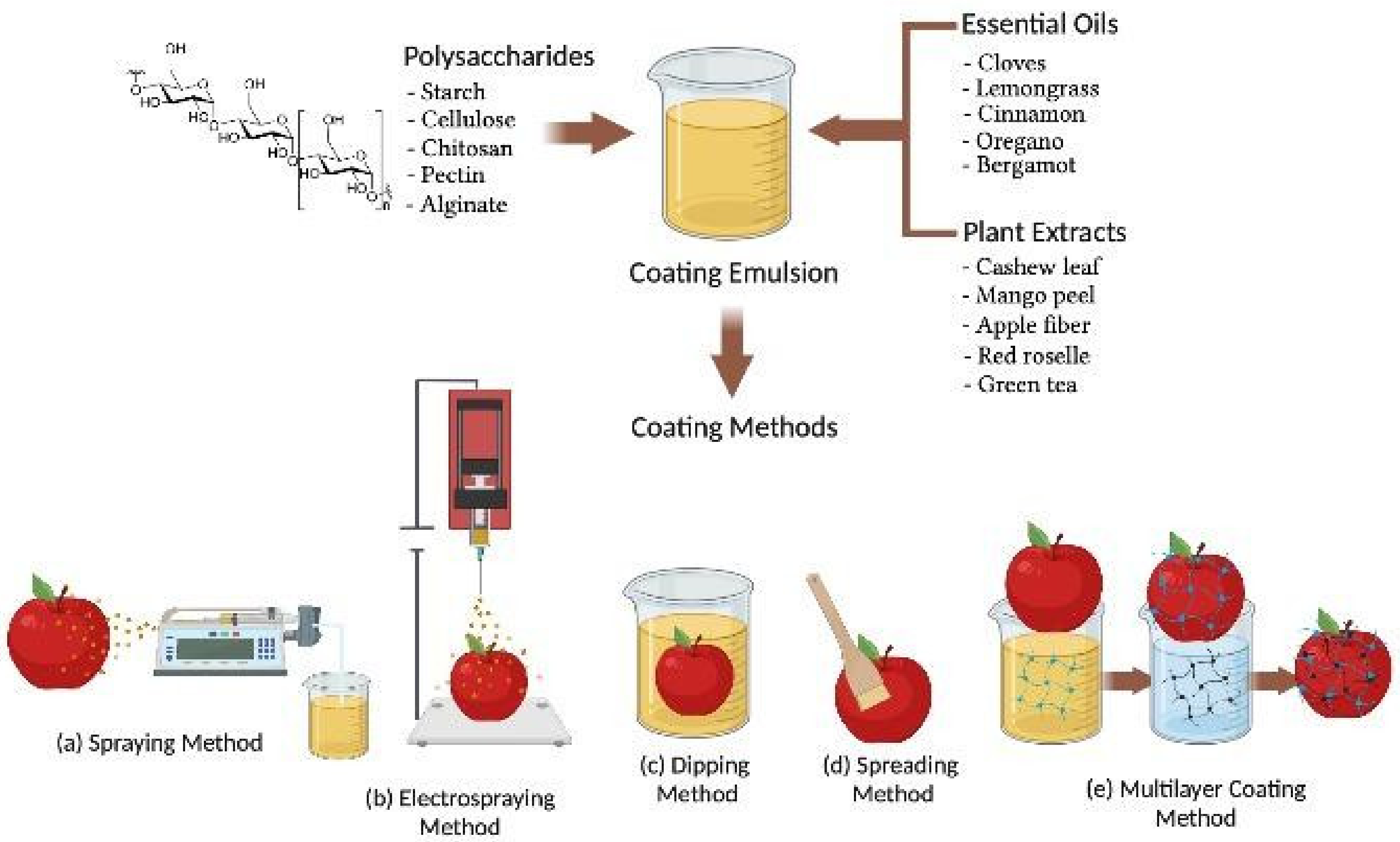
Coatings Free Full Text Polysaccharide Based Active Coatings Incorporated With Bioactive Compounds For Reducing Postharvest Losses Of Fresh Fruits Html

Plant Gums As The Functional Compounds For Edible Films And Coatings In The Food Industry A Review Khezerlou 2021 Polymers For Advanced Technologies Wiley Online Library

Pdf Superhydrophobic Coatings With Edible Biowaxes For Reducing Or Eliminating Liquid Residues Of Foods And Drinks In Containers

Release Process In Edible Coatings Incorporated With Functionalized Download Scientific Diagram

Superhydrophobic Coatings From Beeswax Advanced Science News

A New Approach In The Hydrophobic Modification Of Polysaccharide Based Edible Films Using Structured Oil Nanoparticles Sciencedirect

Fabrication Of Superhydrophobic Coatings With Edible Materials For Super Repelling Non Newtonian Liquid Foods Sciencedirect
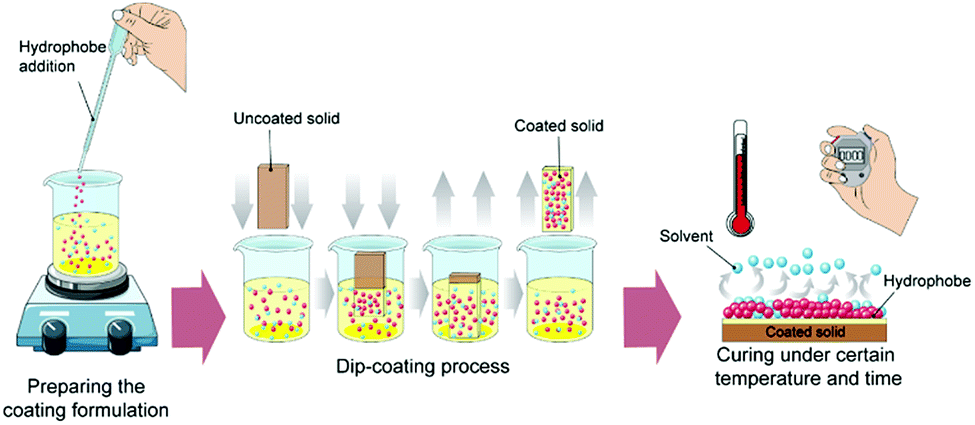
Bio Inspired Sustainable And Durable Superhydrophobic Materials From Nature To Market Journal Of Materials Chemistry A Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C9ta05185f



Comments
Post a Comment